Boiler Energy-Efficient
Whether you have a steam or hot water boiler, energy efficiency is an important factor in how much money your heating system costs. The best way to save on energy bills is by installing a high-efficiency boiler. However, there are also other factors that can have an impact on a boiler’s energy efficiency. These include insulating the system properly, upgrading blowdown heat recovery systems and ensuring that the system is sized appropriately.
Boiler energy efficiency is based on how well heat is transferred from fuel to steam. The best way to improve this is by reducing the temperature of steam at the point of discharge. This is often done by using low-temperature applications for steam that only need a lower grade of heat, and redirecting the exhaust heat from higher-grade processes to lower-temperature applications. This technique reduces both energy costs and emissions.
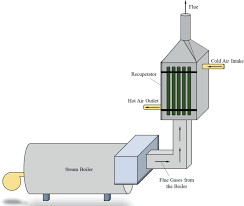
The most significant source of Energy Efficient Steam Boiler inefficiency comes from flue gas losses, which occurs when the combustion process loses heat to the surrounding air. This heat loss is a result of poor combustion, excess air levels and unburned carbon (as a percentage of the total combustible fuel).
What Makes a Boiler Energy-Efficient?
A boiler’s energy efficiency can be measured by its annual fuel utilization efficiency (AFUE) rating. This indicates how efficiently the fuel is converted to heat energy. The higher the AFUE rating, the better. A typical conventional boiler has an AFUE of around 80 to 85 percent, with 15 to 20 cents of every dollar spent on fuel being lost in the form of hot exhaust and venting gases.
High-efficiency boilers use a technology called condensing to extract more heat from the combustion process, resulting in lower stack temperatures and less wasted fuel. This is why they are sometimes referred to as condensing boilers.
One of the key strategies employed in the development of energy-efficient steam boilers involves enhancing thermal efficiency through improved combustion techniques and heat transfer mechanisms. Modern steam boilers integrate sophisticated combustion control systems, such as advanced burner designs and intelligent fuel management systems, to optimize the combustion process and minimize energy losses. Additionally, innovative heat exchanger designs, including enhanced surface area configurations and optimized flow patterns, enable more efficient heat transfer from the combustion gases to the boiler’s water or steam, thereby maximizing thermal efficiency.
Another way to increase a boiler’s energy efficiency is by installing an economizer. These systems capture the waste heat from a boiler’s flue gases and reuse it by preheating incoming feedwater. This significantly decreases the amount of heat energy that is needed to generate steam and hot water.
Choosing the right size boiler for your home can have an important impact on your energy bills. A boiler that is too large will use more fuel to heat the house, and one that’s too small will use less fuel but produce more unwanted heat.
A combi boiler, which makes hot water on demand, is usually the most energy-efficient option for smaller properties with limited space. However, if you have a larger property or a family, a system or conventional boiler may be more suitable to meet your needs while keeping your bills as low as possible.